While running ns2, we always get the same results as much we run with the same parameters. If we need to get different results for running with same parameters,we need to add some random property in our scripting. By using this property, we can check what goes wrong at an exact point. Normally in ns2, simulations are under three categories;
DETERMINISTIC SETTING
This setting is the default setting of ns2 and we get the same output in every run. This simulation scenario is usually convenient for debugging process and to locate errors that occurred in simulation codes or to study about complex nature of networks. So while running in deterministic setting, we will get same results on every time and which helps easy to analysis.
RANDOM SETTING
In case of a statistical analysis, we are forced to simulate a simulation scenario several times and to find out mean & variance. By using deterministic setting we are not able to do this because the variance is zero for that. So we have to provide randomness with every simulation running. This is done by using RNG [Random Number Generator]. This randomness is in two forms;
Single Stream Random Setting
By default, ns2 always have defaultRNG with seed value one(1). To provide randomness, we have to seed different simulation runs differently. In single stream random setting, we need only one RNG and we set different runs with different outputs by providing different values of "k". i.e;
$defaultRNG seed <k>
and random generator use this seed value <k> as seed for generating randomness.
TCL SCRIPT:
$defaultRNG seed 101
set arrivalRNG [new RNG]
set arrival_ [new RandomVariable/Exponential]
$arrival_ set avg_ 5
$arrival_ use-rng $arrivalRNG
puts "Inter-arrival time Packet size"
for {set j 0} {$j < 5} {incr j} {
puts [format "%f " [$arrival_ value] ]
}
OUTPUT:
Inter-arrival time
.056
.234
.090
.678
.456
DESCRIPTION:
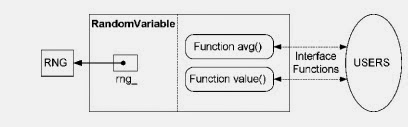
Here, a exponential random variable arrival_ is created and its parameters are provided in the following line. For specifying a RNG, we use OTCL command use-rng and to print the result we used command value.
 |
| Schematic Diagram |
Multiple Stream Random Setting
If we need more than one variable to provide randomness in simulation runs,we have to create different set of new RNG as per our requirements.
REFERENCE:
Introduction to Network Simulator NS2 by Teerawat Issariyakul • Ekram Hossain; 2nd Edition
Comments
Post a Comment