AWK Script
AWK is a high level programming language which is used to process text files,named after its three orginal author's name:
A : Alfred Aho
W : Peter Weinberger
K : Brian Kernighan
AWK Scripts are very good in processing the data from the log (trace files) which we get from NS2. If you want to process the trace file manually.
AWK PROGRAM STRUCTURE
Awk program structure contains mainly three parts;
1. Begin
2. Content
3. End
BEGIN {<initialization>}
<pattern1> {<actionSet1>}
<pattern2> {<actionSet2>}
. . .
END {<final finalActionSet>}
BEGIN : Begin deals with what to be executed prior to text file processing,normally which is used to initialize variable values or constants.
CONTENT : Script which process the text file. In this part, AWK moves lines by lines (i.e., records by records) and executes the <actionSet> if the current line match with the pattern. The actions repeats until AWK reaches the end of the file.
END : This part explains what to be executed after the text file processing ie. what to print on the terminal or to show output in terminal.
EXECUTION
Awk has two types of execution;
1) Plain Execution.
2) Match and Execute.
Plain Execution : Simply AWK statements.
Match and execute : The second type of execution is “Match and Execute”, when executes plain execution statements only if the current line (of the input text file) matches with a predefined pattern. The pattern can be either : 1. Logical Expression 2. Regular Expression.
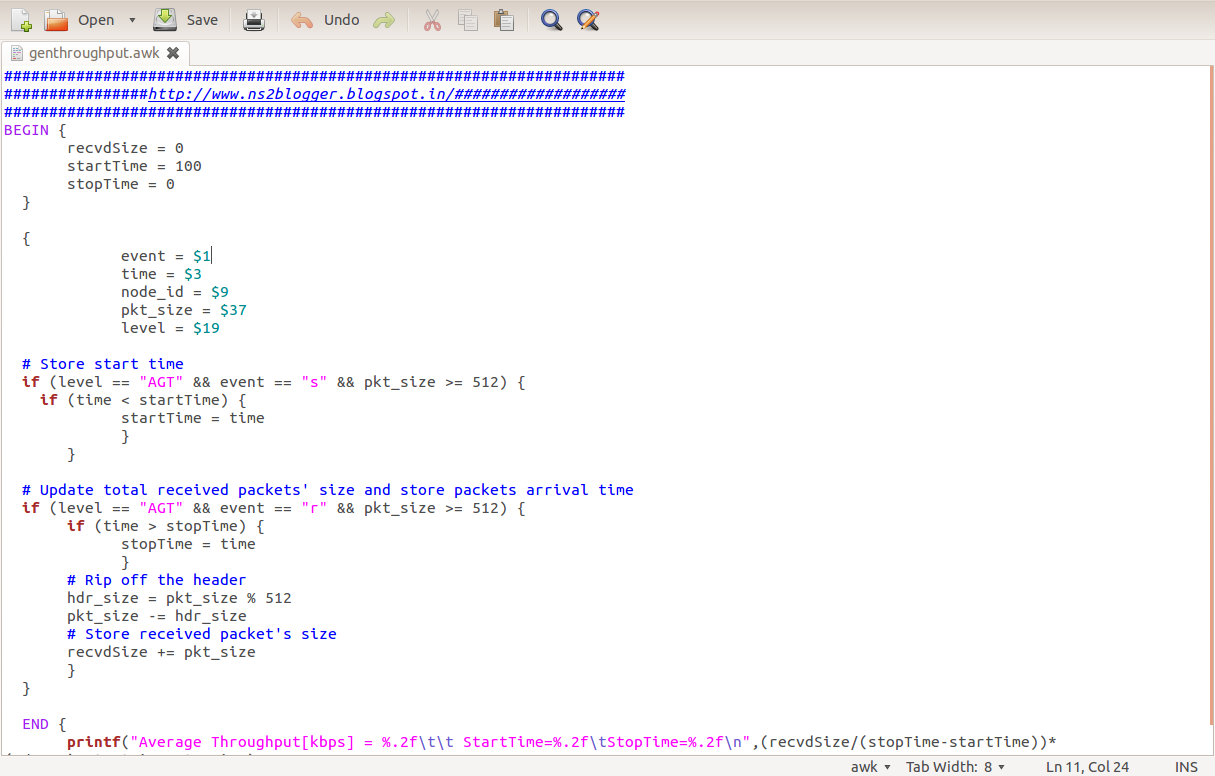 |
| Sample Awk Script |
TRACE FILE AND AWK SCRIPT
Here is a sample of trace file from NS2 , to know more about trace file click here
AWK Scripts are very good in processing the data column wise. For example the first column in the above trace file represents r, s which indicates receive, sent respectively. If we want to trace the entire r and s alone from this trace file we can represent it as $1
So
$1 : Action (r,s,d.f)
$2 Time
$3 Time value
$4 node id
$5 node id value
$6 id of next hop
$7 next hop id value
.
.
.
.
More description of trace file is in above link.
To run awk script, we have to use terminal window.
For that first we have to install gawk in Linux.for that we have to write following code in terminal;
sudo apt-get install gawk

after installing gawk, we have to run the awk script using command;
gawk -f <awk file name> <trace file name>
gawk -f file.awk file.tr
The ‘-f’ instructs the awk utility to get the awk program from the source file i.e from .awk file.
After entering command you will get values.
AWK SCRIPTS
1. For calculating Throughput, Click here
2. For calculating End to End Delay,Routing Load and Packet Density Fraction, Click here
3. For calculating Jitter, Click here
4. For calculating energy, Click here
5. For calculating network statistics, Click here
6. For printing congestion window, Click here
7. For calculating all network statistics, Click here
8. For calculating final node position and energy of node, Click here
Note :
1. This awk script is for new trace format files.
2. Copy this awk files to the directory where tcl script is saved.
3. Change initial values as per your need.
PERL Script
Perl is a general-purpose programming language originally developed for text manipulation and now used for a wide range of tasks including system administration, web development, network programming, GUI development, and more.
The language is intended to be practical (easy to use, efficient, complete) rather than beautiful (tiny, elegant, minimal). Its major features are that it's easy to use, supports both procedural and object-oriented (OO) programming, has powerful built-in support for text processing, and has one of the world's most impressive collections of third-party modules.
Like awk script, perl script can also be used to perform post analysis of trace files. Perl script are simple any tiny than awk scripts.
Alternatively, put this as the first line of your script:
- perl progname.pl
...and run the script as /path/to/script.pl. Of course, it'll need to be executable first, so
- #!/usr/bin/env perl
chmod 755 script.pl (under Unix).(This start line assumes you have the env program. You can also put directly the path to your perl executable, like in
#!/usr/bin/perl ).after running your tcl file copy and paste the perl script to the same directory and then the perl script can be run from your terminal by typing the following command.
perl filename.p tracefilename.tr
1. Perl script for calculating packet sent, packet received, packet dropped, routing overhead, packet delivery ratio and average path length can be downloaded for here. Click here.
2. Perl script to calculate average end to end delay can be downloaded from here. Click here.
Note : Copy and paste this perl script to the directory where tcl script is saved.

Comments
Post a Comment